3D printing techologies
All 3D printing technologies are based on the same principle, which involves gradually layering material on top of each other. However, even in the present day, there is no universal method suitable for all applications. It is necessary to consider what we expect from the printer and what we want to print. The most well-known 3D printing technologies can be divided into three categories based on the form of material printing and its processing:
- Material in the form of filament – material is extruded through a heated nozzle, including FDM and FFF. These can be considered synonymous.
- Liquid material – each layer is cured by a light beam (UV or DLP). This category includes SLA.
- Material in the form of fine powder – material is fused using a laser. Representative technologies include SLS.
1. FDM/FFF
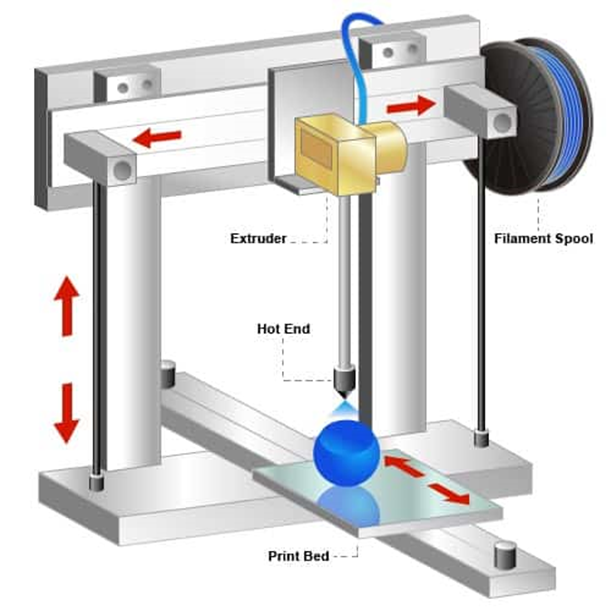
Fused Deposit Modeling or Fused Filament Fabrication is the most widespread and accessible 3D printing technology. It is suitable for printing various models and prototypes. The primary material used is a printing strand called filament, which has a diameter of 1.75 mm. Originally, a 3 mm diameter filament was used, but it was less precise in terms of dosage.
It gained its popularity not only due to its reliability but also because of its relatively understandable mechanics, reminiscent of a melting gun. FDM/FFF operates on a layering principle. The material used is a thermoplastic filament wound onto a spool attached to an extruder[1], which has its own motor and extrudes the filament through a heated nozzle. This nozzle maintains a constant temperature, rapidly melting the filament into a liquid that is then extruded through a small nozzle onto the build platform.
The nozzle moves slightly above the build platform, applying a layer along the X and Y axes. It then moves up along the Z-axis by one layer and continues to apply layers until the entire object is created. Some printers can also move the build platform horizontally.
In today's context, there are printers equipped with multiple extruders for combining filament colours or materials. The most well-known printers in this category are the Prusa printers from Czech manufacturers, which can use up to five extruders simultaneously.